A conical water tank with vertex down – Conical water tanks, with their distinctive shape and vertex pointing downward, offer a unique and practical solution for water storage and management. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of conical water tanks, exploring their volume, surface area, applications, and design considerations.
As we embark on this journey, we will uncover the formula for calculating the volume of a conical water tank, providing a step-by-step guide to determine its capacity. Furthermore, we will explore the factors that influence the volume and capacity of these tanks.
1. Conical Tank Description: A Conical Water Tank With Vertex Down
A conical water tank is a specialized container designed to store liquids, featuring a cone-shaped body with its vertex pointing downwards. This unique geometry provides several advantages for liquid storage applications.
The tank’s shape comprises a circular base and a conical surface that extends upwards from the base to meet at a single point, the vertex. The vertex is positioned at the bottom of the tank, allowing for complete drainage of the stored liquid.
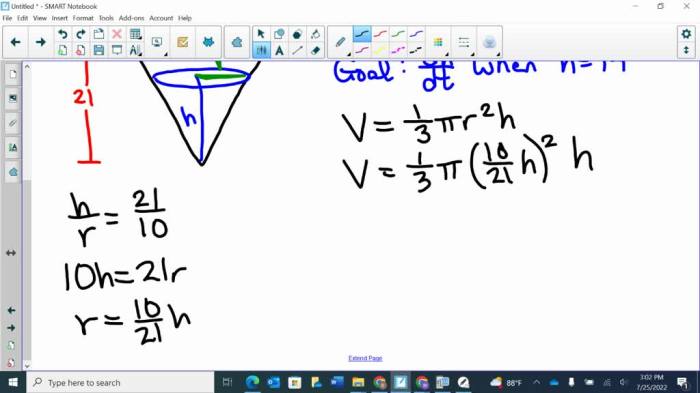
The dimensions of a conical water tank are typically defined by its base radius (r) and its height (h). The base radius determines the width of the tank’s circular base, while the height measures the vertical distance from the base to the vertex.
The orientation of the tank, with its vertex down, ensures that the weight of the stored liquid is evenly distributed across the base, minimizing stress on the tank’s structure.
2. Volume and Capacity
The volume of a conical water tank, which represents the amount of liquid it can hold, is calculated using the formula:
V = (1/3)πr²h
where:
- V is the volume in cubic units (e.g., liters, gallons)
- π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14
- r is the base radius in linear units (e.g., centimeters, inches)
- h is the height in linear units (e.g., centimeters, inches)
To determine the capacity of the tank, simply fill it with liquid and measure the volume using appropriate measuring instruments.
Factors affecting the volume and capacity of a conical water tank include the base radius, height, and the density of the stored liquid.
3. Surface Area

The surface area of a conical water tank, which represents the total area of its exterior surface, is calculated using the formula:
A = πr(r + √(h² + r²))
where:
- A is the surface area in square units (e.g., square meters, square feet)
- π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14
- r is the base radius in linear units (e.g., centimeters, inches)
- h is the height in linear units (e.g., centimeters, inches)
To determine the surface area of the tank, simply measure the base radius and height and substitute these values into the formula.
Factors affecting the surface area of a conical water tank include the base radius, height, and the shape of the cone.
4. Applications and Uses

Conical water tanks find applications in various industries and settings, including:
- Water storage and distribution systems
- Industrial processes
- Chemical storage
- Food and beverage production
- Irrigation and agriculture
Advantages of using conical water tanks include:
- Efficient liquid storage due to their shape
- Easy to clean and maintain
- Durable and long-lasting
Disadvantages of using conical water tanks include:
- May require specialized equipment for installation and maintenance
- Not suitable for storing liquids that require constant agitation
| Conical Water Tanks | Other Water Storage Containers |
|---|---|
| Efficient liquid storage due to their shape | May not be as efficient in space utilization |
| Easy to clean and maintain | May require more complex cleaning procedures |
| Durable and long-lasting | May have shorter lifespans depending on material and usage |
5. Design Considerations
When designing a conical water tank, several factors must be taken into account:
- Materials:Common materials used include stainless steel, fiberglass, and polyethylene.
- Size and Shape:The size and shape of the tank depend on the required capacity and available space.
- Structural Integrity:The tank must be designed to withstand the weight of the stored liquid and external forces.
- Corrosion Resistance:The tank must be made of corrosion-resistant materials or coated to protect against corrosion.
- Access and Maintenance:The tank should have easy access for inspection, cleaning, and maintenance.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers can design conical water tanks that meet specific requirements and ensure optimal performance and longevity.
FAQ Guide
What is the formula for calculating the volume of a conical water tank?
Volume = (1/3)πr²h, where r is the radius of the base and h is the height of the tank.
How do I determine the surface area of a conical water tank?
Surface Area = πr(r + √(r² + h²)), where r is the radius of the base and h is the height of the tank.