Identify the four tectonic settings of igneous activity. – The tectonic settings of igneous activity refer to the different geological environments in which magma rises to the Earth’s surface and crystallizes to form igneous rocks. Understanding these settings is crucial for comprehending the processes that shape our planet and provide valuable insights into the Earth’s geological history.
This comprehensive guide explores the four primary tectonic settings of igneous activity: divergent boundaries, convergent boundaries, transform boundaries, and intraplate settings. Each setting is characterized by unique geological processes and distinct types of igneous activity.
Tectonic Settings of Igneous Activity
Igneous activity, the process of magma solidifying to form rock, occurs in various tectonic settings. These settings are primarily defined by the movement and interactions of tectonic plates, which shape the Earth’s crust and mantle.
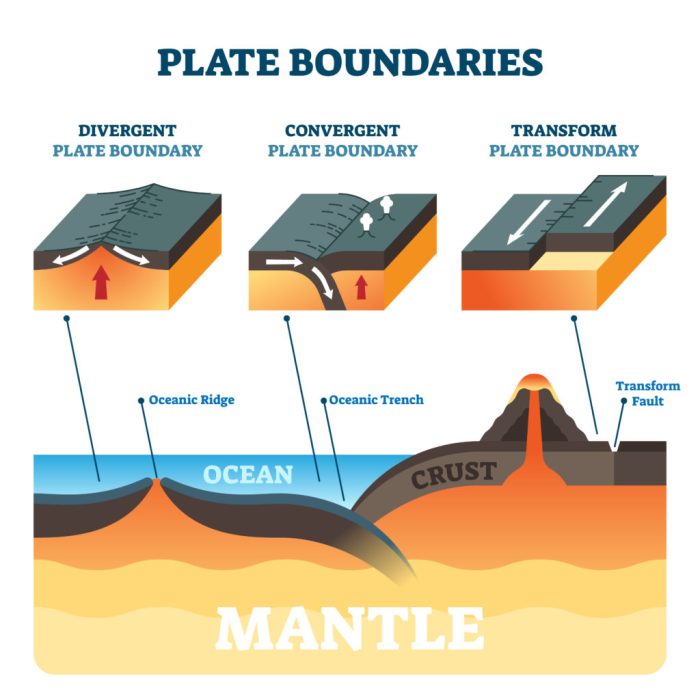
1. Divergent Boundaries
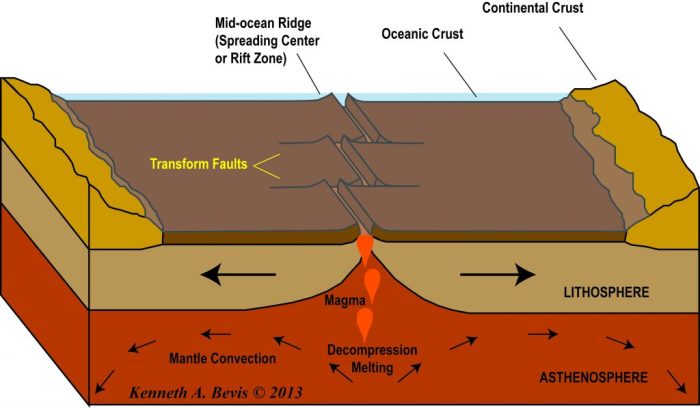
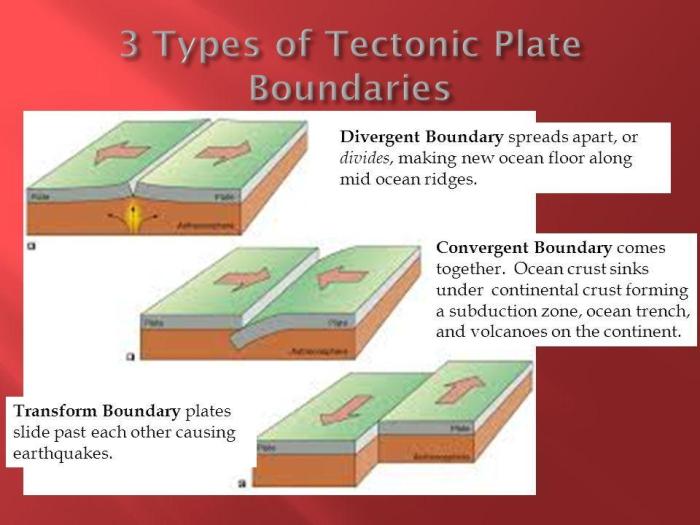
Divergent boundaries are regions where tectonic plates move away from each other. As the plates separate, magma rises from the mantle and fills the gap, creating new oceanic crust.
- Examples of divergent boundaries include the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the East Pacific Rise.
- Igneous activity associated with divergent boundaries typically produces basaltic lava flows and pillow lavas.
2. Convergent Boundaries, Identify the four tectonic settings of igneous activity.
Convergent boundaries are regions where tectonic plates collide. The type of igneous activity that occurs at convergent boundaries depends on the composition and density of the colliding plates.
- Types of convergent boundaries include oceanic-continental, oceanic-oceanic, and continental-continental collisions.
- Igneous activity associated with convergent boundaries can range from the formation of volcanic arcs and batholiths to the subduction of oceanic crust.
3. Transform Boundaries
Transform boundaries are regions where tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally. These boundaries are characterized by strike-slip faults.
- Igneous activity associated with transform boundaries is typically limited to small-scale intrusions and extrusions along the fault lines.
4. Intraplate Settings
Intraplate volcanism occurs within the interior of tectonic plates, away from plate boundaries. This type of igneous activity is often associated with hotspots or mantle plumes.
- Examples of intraplate settings include the Hawaiian Islands and the Yellowstone hotspot.
- Mechanisms responsible for intraplate igneous activity include the upwelling of mantle material and the melting of the overlying crust.
FAQ: Identify The Four Tectonic Settings Of Igneous Activity.
What is the significance of studying the tectonic settings of igneous activity?
Understanding the tectonic settings of igneous activity provides valuable insights into the geological processes that shape our planet, the formation of different types of igneous rocks, and the distribution of mineral resources.
How do divergent boundaries contribute to the formation of new oceanic crust?
At divergent boundaries, tectonic plates move away from each other, causing magma to rise and fill the gap. As the magma cools and crystallizes, it forms new oceanic crust, expanding the ocean floor.
What types of igneous activity are associated with convergent boundaries?
Convergent boundaries, where tectonic plates collide, are characterized by subduction zones and the formation of volcanic arcs. Subduction zones produce magma that rises to the surface and forms volcanoes, while volcanic arcs are chains of volcanoes that develop above subducting oceanic crust.
How do transform boundaries influence igneous activity?
Transform boundaries, where tectonic plates slide past each other, can generate frictional heat that melts rocks. This molten material can rise to the surface and form volcanoes or intrusive igneous bodies.
What are the mechanisms responsible for intraplate igneous activity?
Intraplate igneous activity occurs within the interiors of tectonic plates, away from plate boundaries. It is primarily caused by the upwelling of hot mantle material, which can melt rocks and form volcanoes or intrusive igneous bodies.