Rheumatoid arthritis with joint arthroplasty hesi case study is an intriguing medical narrative that delves into the intricacies of a complex condition and its innovative treatment. This case study provides valuable insights into the challenges faced by patients with rheumatoid arthritis, the surgical intervention of joint arthroplasty, and the multifaceted role of nurses in their care.
The patient’s journey, from diagnosis to recovery, is meticulously documented, offering a comprehensive understanding of the disease’s impact and the effectiveness of joint arthroplasty in restoring mobility and improving quality of life. The case study also highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration, ethical considerations, and patient-centered care in managing rheumatoid arthritis.
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. Joint arthroplasty, also known as joint replacement surgery, is a surgical procedure that involves replacing a damaged or diseased joint with an artificial implant.
This procedure can be an effective treatment option for patients with RA who experience severe joint pain and disability.
This case study examines the use of joint arthroplasty in a patient with RA, discussing the patient’s medical history, surgical intervention, post-operative care, and outcomes.
Patient History and Presentation

The patient is a 65-year-old female with a 10-year history of RA. She is a retired teacher and lives independently. Her symptoms include:
- Joint pain and swelling in her hands, wrists, knees, and ankles
- Morning stiffness that lasts for more than an hour
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
Physical examination reveals joint tenderness, swelling, and limited range of motion. X-rays show joint damage and erosion.
Treatment Plan and Surgical Intervention
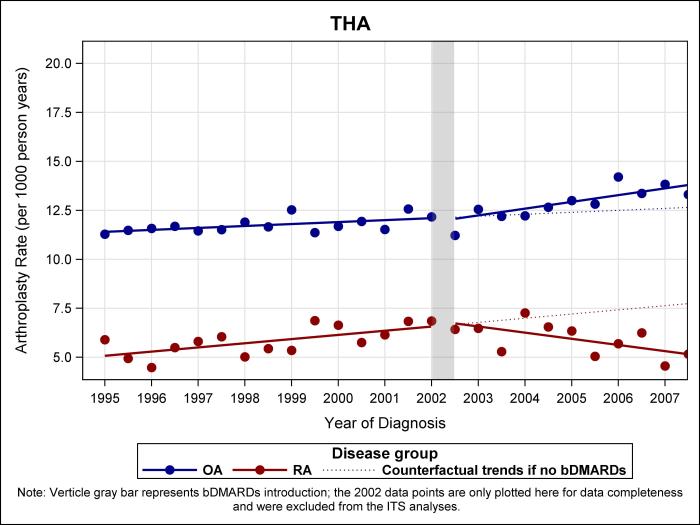
Due to the severity of the patient’s symptoms and the failure of conservative treatment, joint arthroplasty is recommended. The patient undergoes a total knee replacement surgery. The surgery involves removing the damaged joint and replacing it with an artificial implant made of metal and plastic.
The patient’s recovery plan includes pain management, wound care, and physical therapy. She is discharged from the hospital two days after surgery and continues her rehabilitation at home.
Post-Operative Care and Outcomes: Rheumatoid Arthritis With Joint Arthroplasty Hesi Case Study
The patient’s pain is well-controlled with medication. Her wound heals without complications. She attends physical therapy sessions regularly and makes significant progress in regaining range of motion and strength in her knee.
At her six-month follow-up appointment, the patient reports significant improvement in her symptoms. She is able to walk without pain and has returned to her daily activities. She is very satisfied with the outcome of her surgery.
Nursing Implications
Nurses play a crucial role in caring for patients with RA who undergo joint arthroplasty. Responsibilities include:
- Patient education and counseling
- Medication administration
- Wound care
- Pain management
- Monitoring progress and providing support
Nurses must be knowledgeable about the disease process, surgical procedure, and post-operative care to provide optimal care for these patients.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical issues related to this case study include:
- Patient autonomy and informed consent
- Resource allocation
It is important to respect the patient’s values and preferences and to ensure that they are fully informed about the risks and benefits of surgery before making a decision.
Resource allocation must also be considered, as joint arthroplasty is a costly procedure. It is important to ensure that patients who are most likely to benefit from surgery are given priority.
FAQ Summary
What is the primary goal of joint arthroplasty in rheumatoid arthritis?
The primary goal of joint arthroplasty in rheumatoid arthritis is to alleviate pain, restore joint function, and improve the patient’s quality of life.
What are the potential risks and complications associated with joint arthroplasty?
Potential risks and complications include infection, bleeding, blood clots, nerve damage, and implant failure.
What is the role of nurses in caring for patients with rheumatoid arthritis undergoing joint arthroplasty?
Nurses play a crucial role in providing patient education, wound care, pain management, and rehabilitation support throughout the pre- and post-operative phases.